 Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness. Sometimes called the silent thief of sight, glaucoma can damage your vision so gradually you don’t notice any loss of vision until the disease is at an advanced stage. Vision experts believe that half of those affected by glaucoma may not know it, since there are usually no symptoms in its early stages. By the time an individual notices something is wrong, the disease has already caused considerable damage. Vision lost to glaucoma cannot be regained. Although there is no cure, medications and surgery can help slow the disease’s progression.
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness. Sometimes called the silent thief of sight, glaucoma can damage your vision so gradually you don’t notice any loss of vision until the disease is at an advanced stage. Vision experts believe that half of those affected by glaucoma may not know it, since there are usually no symptoms in its early stages. By the time an individual notices something is wrong, the disease has already caused considerable damage. Vision lost to glaucoma cannot be regained. Although there is no cure, medications and surgery can help slow the disease’s progression.
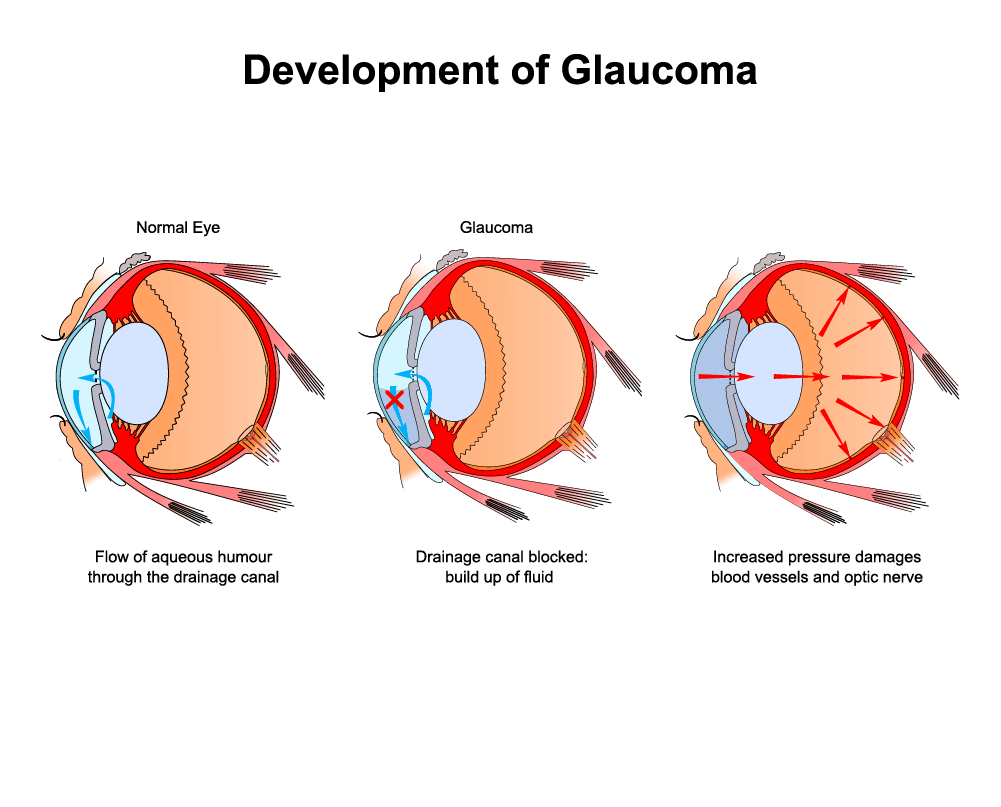
Glaucoma is actually a group of eye diseases that lead to damage of the optic nerve (the bundle of nerve fibers that carries information from the eye to the brain), which can then lead to vision loss and possibly blindness. Optic nerve damage usually occurs in the presence of high eye (intraocular) pressure.
Types of Glaucoma
There are many types of glaucoma, but the two most common types are open-angle glaucoma and closed angle (angle-closure) glaucoma.
Open-angle glaucoma, (also called primary open-angle glaucoma and chronic glaucoma) accounts for 90 percent of all glaucoma cases and occurs when the trabecular meshwork becomes blocked and the fluid can’t get to the normal drainage canals. This blockage results in fluid build-up and intraocular pressure. The fluid build-up happens gradually.
Closed angle glaucoma, (also called acute glaucoma or angle closure glaucoma), accounts for about 9 percent of all glaucoma cases and occurs when the opening between the cornea and iris narrows, such that the fluid cannot get to the trabecular meshwork and normal drainage channels. This narrowing results in fluid build-up and intraocular pressure. The fluid build-up happens very quickly.
People at highest risk are those with any of the following:
- Age older than 40
- African-American race
- Family members who have (or had) the disease
- Farsightedness or nearsightedness
- Diabetes
- Long-term use of corticosteroid drugs
- Previous eye injury
Glaucoma is a slow progressing eye disease. These are symptoms one may encounter as it progresses:
- Tiny blind spots appear at the edges of the visual field (peripheral or side vision) that slowly get larger and spread
- Blurred vision
- Appearance of colored halos around lights
- Adjustment problems on entering a dark room
- Repeated difficulties that new eyeglass prescriptions do not help
- Peripheral (side) vision is decreasing
The symptoms of closed angle glaucoma are:
- Severely blurred vision
- Severe eye and head pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Appearance of rainbow-colored halos around bright lights
- Rapid loss of vision





